Contents
Contributors
Preface
1 Current State and Future Potential of Global Food Production and Consumption
Introduction
Global Food Production
Global Food Consumption
Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency in Agriculatural Production
Conclusions
2 Water Resources and Global Change
Introduction
Observed Global Trends in Precipitation and Temperature
Future Trends in Precipitation and Temperature
Future Trends in Water Availability
Consequences for Agricultural Production
Uncertainties in Climate Change Projections
3 Translating Water into Food: How Water Cycles in Natural and Agricultural Landscapes
Introduction
Physical Basis of Water Cycling
Water Needs for Food Production
Water Fluxes in Agricultural Landscape
Impact of Landscape Structure on Water Cycling
Improvement of Water Management in Agricultural Landscapes
Conclusions
4 Nutrients as Limited Resources: Global Trends in Fertilizer Production and Use
Fertilizer Consumption
Fertilizer Supply
Resource Management
Challenges Facing the Fertilizer Industry
5 The Flow of Phosphorus in Food Production and Consumption Systems
The Use of Phosphorus in Global Food Production
Key Challenges: Scarcity and Pollution
Sustainable Pathways for Future Phosphorus Flows
The Road Ahead
6 Matching Soil Nutrient Supply and Crop Demand during the Growing Season
Introduction
Soil Supply of Nutrients
Crop Nutrient Demand
Matching Supply to Demand
Conclusions
7 Physiology of Nitrogen-Use Efficiency
Introduction
Nutrient Uptake and Use
Nitrogen-Use Efficiency
Nitrogen Remobilization
Molecular Approach for Increasing N-Use Efficiency
Conclusions
8 Improving Crop Nitrogen Use in Dryland Farming: Interactions and Potential Trade-offs between Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency
Introduction
Improving Productivity Under Limited Water Availability (Increasing WUE)
Improving N-Use Efficiency
Interactions/Trade-offs between N-Use and Water-Use Efficiencies
Maximizing N-Use and Water-Use Efficiencies
Conclusions
9 Breeding Approaches to Increasing Water-Use Efficiency
Introduction
Evaluation of WUE
Inheritance of WUE
Breeding for WUE
Conclusions And Future Prospects
10 Breeding Approaches to Increasing Nutrient-Use Efficiency: Examples from Common Beans
Introduction
Nutrient-Use Efficiency
Breeding Strategies
Final Reflections
Acknowledgments
11 Using Simulation Modeling of Root Growth and Function as an Aid in Breeding for Increased Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency
Efficient Root Systems
Some Existing Architectural Root Models
Examples of the Use of Root Architecture and Development Models
Areas where a Modeling Approach could be Usefully Applied
Conclusions
12 Improving Crop Production in the Arid Mediterranean Climate
Introduction
Multiple Abiotic Stresses
Water-Saving Irrigation Strategies
A Framework for Biological Water Saving
Dryland Agriculture in the Mediterranean Region
Advancing Agricultural Practices in Dryland Mediterranean Farming
Selection and Breeding in Mediterranean Region
Concluding Remarks
13 Agronomic Principles of Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency: Case Studies in Dryland Grain Production in Australia
Introduction
Resource-Use Efficiency: Concepts and Definitions
Agronomic Opportunities to Increase Resource-Use Efficiency
Case Studies in Efficient Resource Use at Different Spatial Scales
Summary and Conclusions
14 Use of Organic Fertilizers Alone or in Combination with Inorganic Ones: Effects on Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency in Indian Farming Systems
Introduction
Improving Nutrient-Use Efficiency
Global Status of N-Use Efficiency
Water-Nutrient Interactions: Key Issue in Increasing Use Efficiency
Integrated Nutrient Management—Toward Improving Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency
Conclusions
15 Current Status and Future Perspectives to Increase Nutrient- and Water-Use Efficiency in Food Production Systems in China
Historical Changes and Future Challenge of Crop Production
The Current Status of Fertilizer- and Water-Use Efficiency
Future Perspectives for Increasing Nutrient- and Water-Use Efficiency
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
16 Water- and Nutrient-Use Efficiency in Food Production in South America
Introduction
Major Soil Groups in South America
Cropping Systems in South America
Water-Use Efficiency
Nutrient Uptake by Crop Plants
Nutrient-Use Efficiency in Crop Plants
Conclusions
Index

This edition first published 2013 © 2013 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Wiley-Blackwell is an imprint of John Wiley & Sons, formed by the merger of Wiley’s global Scientific, Technical and Medical business with Blackwell Publishing.
Editorial Offices
2121 State Avenue, Ames, Iowa 50014-8300, USA
The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 8SQ, UK
9600 Garsington Road, Oxford, OX4 2DQ, UK
For details of our global editorial offices, for customer services and for information about how to apply for permission to reuse the copyright material in this book please see our website at www.wiley.com/wiley-blackwell.
Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal or personal use of specific clients, is granted by Blackwell Publishing, provided that the base fee is paid directly to the Copyright Clearance Center, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923. For those organizations that have been granted a photocopy license by CCC, a separate system of payments has been arranged. The fee codes for users of the Transactional Reporting Service are ISBN-13: 978-0-8138-1989-1/2013.
Designations used by companies to distinguish their products are often claimed as trademarks. All brand names and product names used in this book are trade names, service marks, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. The publisher is not associated with any product or vendor mentioned in this book.
Limit of Liability/Disclaimer of Warranty: While the publisher and author(s) have used their best efforts in preparing this book, they make no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this book and specifically disclaim any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. It is sold on the understanding that the publisher is not engaged in rendering professional services and neither the publisher nor the author shall be liable for damages arising herefrom. If professional advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Improving water and nutrient use efficiency in food production systems / editor, Zed Rengel.
pages cm
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN 978-0-8138-1989-1 (hardback : alk. paper)
1. Crops–Water requirements. 2. Crops–Nutrition. 3. Water conservation. 4. Fertilizers.
5. Plant nutrients. I. Rengel, Zdenko.
S494.5.W3I47 2013
631.5′82–dc23
2012038415
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.
Wiley also publishes its books in a variety of electronic formats. Some content that appears in print may not be available in electronic books.
Cover design by Nicole Teut
Lotta Andersson | Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Norrköping, Sweden |
Matthew W. Blair | Universidad Nacional de Colombia–Palmira Palmira, Colombia and Cornell University Department of Plant Breeding Ithaca, New York |
Bill Bowden | Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) & Department of Agriculture and Food Western Australia (DAFWA) The Leeuwin Centre Floreat Park, Australia |
Dana Cordell | Institute for Sustainable Futures University of Technology Sydney Broadway, New South Wales, Australia |
Art J. Diggle | Department of Agriculture and Food Western Australia, Bentley, Australia |
Vanessa M. Dunbabin | Tasmanian Institute of Agricultural Research University of Tasmania Hobart, Tasmania, Australia |
Nand K. Fageria | National Rice and Bean Research Center of Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (EMBRAPA) Santo Antônio de Goiás, Goiás State, Brazil |
Mingsheng Fan | Department of Plant Nutrition China Agricultural University Key Laboratory of Plant-Soil Interactions Ministry of Education Beijing, China |
Trevor P. Garnett | Australian Centre for Plant Functional Genomics (ACPFG) University of Adelaide, Waite Campus Glen Osmind, Australia |
Patrick Heffer | International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA) Paris, France |
Dattatreya Mahabaleswara Hegde | Directorate of Oil Seed Research Rajendranagar Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India |
Christine Heumesser | Institute for Sustainable Economic Development University of Natural Resources and Life Science Vienna, Austria |
Sven-Erik Jacobsen | Faculty of Life Sciences University of Copenhagen Tåstrup, Denmark |
Christian Richardt Jensen | Faculty of Life Sciences University of Copenhagen Tåstrup, Denmark |
Andrzej Kędziora | Institute for Agricultural and Forest Environment Polish Academy of Sciences Poznań, Poland |
John A. Kirkegaard | Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) Sustainable Agriculture Flagship CSIRO Plant Industry Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia |
Sumanta Kundu | Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture Santoshnagar, Saidabad Post Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India |
Zbigniew W. Kundzewicz | Institute for Agricultural and Forest Environment Polish Academy of Sciences Poznań, Poland and Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Potsdam, Germany |
Fulai Liu | Faculty of Life Sciences University of Copenhagen Tåstrup, Denmark |
Al Imran Malik | School of Earth and Environment Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Science The UWA Institute of Agriculture The University of Western Australia Crawley, Australia |
Lianne Merchuk | The Hebrew University of Jerusalem The Robert H. Smith Institute of Plant Sciences and Genetics in Agriculture Rehovot, Israel |
Tina-Simone S. Neset | Centre for Climate Science and Policy Research Department of Water and Environmental Studies Linköping University Linköping, Sweden |
Michel Prud’homme | International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA) Paris, France |
K. Venkateswara Rao | Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture Santoshnagar, Saidabad Post Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India |
Greg J. Rebetzke | Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) Plant Industry Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia |
Zed Rengel | School of Earth and Environment Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Science The UWA Institute of Agriculture The University of Western Australia Crawley, Australia |
Michael J. Robertson | Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) Sustainable Agriculture Flagship CSIRO Plant IndustryCanberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia |
Terry Rose | Southern Cross Plant Science Southern Cross University Lismore, New South Wales, Australia |
Yehoshua Saranga | The Hebrew University of Jerusalem The Robert H. Smith Institute of Plant Sciences and Genetics in AgricultureRehovot, Israel |
Erwin Schmid | Institute for Sustainable Economic Development University of Natural Resources and Life Science Vienna, Austria |
Martin Schönhart | Institute for Sustainable Economic Development University of Natural Resources and Life Science Vienna, Austria |
Cherkumalli Srinivasarao | Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture Santoshnagar, Saidabad Post Hyderabad Andhra Pradesh, India |
Luís F. Stone | National Rice and Bean Research Center of Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (EMBRAPA) Santo Antônio de Goiás, Goiás State, Brazil |
Simon Thaler | Centre for Water Resource Systems Institute for Water Quality, Resources and Waste Management Vienna University of Technology Vienna, Austria |
Bandi Venkateswarlu | Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture Santoshnagar, Saidabad Post Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India |
Martin Wegehenkel | Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research Muencheberg, Germany |
Lixing Yuan | Department of Plant Nutrition China Agricultural University Key Laboratory of Plant-Soil Interactions Ministry of Education Beijing, China |
Fusuo Zhang | Department of Plant Nutrition China Agricultural University Key Laboratory of Plant-Soil Interactions Ministry of Education Beijing, China |
Weifeng Zhang | Department of Plant Nutrition China Agricultural University Key Laboratory of Plant-Soil Interactions Ministry of Education Beijing, China |
Xiying Zhang | Center for Agricultural Resources Research Institute of Genetics and Developments Biology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shijiazhuang Hebei, China |
With a world population having reached 7 billion in 2012, and with projections of a 50% increase in the next four decades, coupled with expected increases in the living standards and increased demand for milk and dairy products by a greater proportion of the world population, agriculture is faced with a huge challenge to double the food production in the next 40 years, but on a shrinking area of farmland. Providing food, feed, and fiber for the increasing population on this planet will also need to be achieved using declining water and nutrient resources. In many parts of the world, there is a severe shortage of good quality water that is to be used for irrigation, which is at least partly caused by increased frequency and severity of droughts in the rain-fed, food-producing areas as a result of climate change and variability. On the other side of the issue, raw materials used in producing some fertilizers (e.g., phosphorus [P] and potassium [K]) are becoming scarce and expensive, and the price of energy is also high (production of nitrogen [N] fertilizers is particularly energy demanding), pushing fertilizer prices up. As a result, agriculture must produce more food with lower water and nutrient input; therefore, increased water- and nutrient-use efficiency is of utmost importance.
Increasing efficiency of water and nutrient use (i.e., increasing food production per unit of water and nutrient input) will be crucial in (a) maintaining food security and food quality for increased global population as well as (b) decreasing potentially negative environmental impacts of growing food. In covering both water- and nutrient-use efficiency, this book takes a broad approach that includes social, economic, political, and agronomic aspects of maximizing water- and nutrient-use efficiency in food production, while maintaining healthy natural ecosystems.
The first five chapters provide a global context in which increased efficiencies of water and nutrient use need to be achieved. Historical perspectives are coupled with the regional case studies as well as future projections in terms of changing and variable climate and the population growth effects as they bear not just on increasing food production, but also on doing it sustainably. The food production and consumption patterns are also assessed. The past, present, and the future of fertilizer production and demand are analyzed. A particular emphasis is placed on the water and phosphorus cycling in agricultural and natural landscapes.
Chapters 6 to 11 deal with various agronomic means of improving water- and nutrient-use efficiency in food and feed production, with a strong emphasis on genetics and breeding. The basics of soil nutrient supply and crop nutrient demand (and how to match the two) are covered first, followed by physiology and genetics of nitrogen-use efficiency, and then breeding for water- and nutrient-use efficiency. Given the importance of roots in accessing water and nutrients, an attempt to aid breeding for important root traits by using three-dimensional computer models of root structure and function is particularly interesting.
The remaining five chapters (12 to 16) cover a range of issues relevant to increasing water- and nutrient-use efficiency in a variety of food-producing systems, from arid Mediterranean regions in Europe, Africa, and Australia to two most populous countries in the world, China and India, and to the country with the largest fresh-water resources in the world, Brazil.
This book is intended to provide professionals, students, and administrators with in-depth view of various aspects of water- and nutrient-use in production of food, feed, and fiber. The book takes a multidisciplinary approach in covering issues ranging from political, economic, and social to agronomic. Hence, professionals and scholars working in food policy, environmental regulation, and land conservation as well as agronomists, horticulturalists, plant and soil scientists, geneticists, breeders, soil microbiologists, and others may find an interest in the book.
All chapters have been reviewed according to the standards of international scientific journals. I would like to thank the authors for patiently revising the chapters, sometimes repeatedly, to meet the high standards.
Zed Rengel
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimated the number of undernourished people in the world to be 925 million in 2010, which was 98 million below 2009 levels (FAO 2010c). Hence, more than 1 in 7 people live on a caloric intake below the minimum dietary energy requirement needed for light physical activity. However, the share of hungry people in the world has been declining since the mid-1990s and is at present below the 1970 level (FAO 2009c).
By 2050, global population is projected to reach 9 billion people (United Nations 2009). The continued population growth and the increasing per capita real income will further increase a total food demand for the next 40 years, with changing dietary patterns toward higher proportions of meat, dairy, and fish as well as processed food (Godfray et al. 2010). FAO (2009a) estimated that the current global food production needs to increase by 70% to meet the total food demand in 2050. On average, global agricultural production is projected to grow at 1.7% in the current decade, compared with 2.6% in the first decade of the 21st century (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD] and FAO 2011).
Meeting the increasing food demand is an unprecedented challenge. Even if attainable under the prospect of changing climate and decreasing growth rates of crop yields (Bruinsma 2003; Schmidhuber & Tubiello 2007), it will be difficult without severely exploiting and degrading natural resources, such as land, water, mineral nutrients, and fossil fuels. Additionally, the price hike of commodities and basic staples from 2006 onward and the subsequent financial and economic crisis from 2009 have drastically affected the number of people suffering from hunger and undernourishment (FAO 2009c). High commodity prices increased aggregated consumer price inflation, reduced purchasing power of poor populations, and negatively affected economic stability and food security (FAO-OECD 2011). For many developing countries, the global economic crisis led to a reduction in export earnings, remittances, foreign direct investment, and foreign aid, which led to employment and income losses (FAO 2009c). The price developments were driven by the connection between the agricultural and energy markets, increasing demands for cereals and oilseeds for biofuel production, weather-induced shortfalls of some food products, historically low grain stockpiles, a declining US dollar, increasing agricultural costs of production, and growing foreign exchange holdings by major food-importing countries (Trostle 2008).
Food security does not only encompass food availability and supply, but it also includes food access (which is determined by political, social, and economic arrangements), food use, and food stability (FAO 2006). In this chapter, we focus on food availability and supply by investigating the current state of, and the future potential for, global, resource-efficient food production and consumption.
We first identify options and challenges in increasing global food production. This includes the expansion of agricultural land and competing usage paths (i.e., food, feed, biofuel, and nature conservation as well as increasing agricultural production by intensifying crop management). Furthermore, we discuss the impacts of changing climate and weather patterns on food production together with the options to decrease food demands by changes in human consumption behavior (i.e., less meat in the diet and reducing food waste). In addition, we provide an overview of the trends and challenges concerning the efficiency of water and nutrient use that will be a crucial factor in managing competing uses (i.e., food, feed, fiber, and biofuel) as well as negative environmental externalities.
In this section we contrast frequently raised options and challenges to meet the increasing global food demand. We investigate the supply side of the global food production, focusing on the expansion of agricultural land and the productivity growth, in particular through use of fertilizers, irrigation, and biotechnology. We also account for climate change as an overarching challenge, affecting the future production strategies.
The world’s total land area amounts to approximately 13 billion ha, of which approximately 5 billion ha (38.5%) are agricultural land. Of that land only 1.4 billion ha (28.6%) are arable land (FAO 2010a). Historically, the expansion of agricultural land has been a way to meet the rising food demand. From the 1960s onward, however, food production has been decoupled from cropland expansion as a result of considerable productivity increases (Lambin et al. 2003). Between the early 1960s and the late 1990s, arable land and land under permanent crops expanded by 155 million ha, or 11%, while world population almost doubled. Arable land per person fell by 40% from 0.43 ha to 0.26 ha on average, but land productivity growth through intensification compensated for this reduction in area per person (Bruinsma 2003).
To meet the increasing food demand, a remaining question is whether further expansions in agricultural land are necessary as well ecologically and socioeconomically feasible.
The causes of land use change and agricultural land expansion are manifold and complex, involving situation-specific interactions among a large number of factors at different spatial and temporal scales (Geist & Lambin 2002; Lambin et al. 2003; Smith et al. 2010). Lambin et al. (2003) identified five high-level causes of land use change: (1) resource scarcity and related pressures on natural resources, (2) changing market opportunities, (3) outside policy interventions, (4) loss of adaptive capacity and increased vulnerability of local land users, and (5) changes in social organizations, institutions, and human attitudes. Also, Smith et al. (2010) identified socioeconomic, technological and institutional factors, and social trends, such as population growth and urbanization, as the underlying causes for competition for land. These factors determine the extent of direct pressures on land, which include land transition (e.g., forest clearing to grow crops and pastures), land degradation (e.g., logging, induced fires or overgrazing), and natural causes (e.g., climate change and water availability).
Growing crops for bioenergy has been identified as potential competitor to food production, potentially risking the displacement of forests and grasslands through direct and indirect land use change effects. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimated that energy crop production took place on 1% of global arable land in 2004 and may increase to between 2% and 3.8% by 2030 because biofuel legislation in several countries supports its expansion. The European Union and North America are predicted to experience the largest growth in the area under biofuel crops, from 1.2% of arable land in 2004 to 11.6% in 2030 (EU), with corresponding numbers for the United States of 1.9% to 5.4%. Comparatively, the land requirements for biofuel production in other parts of the world might increase from 0.1% to 2.7% of arable land in 2030 (IEA 2006). The degree of competition can be reduced by technological progress in biofuel conversion technologies and a switch to second-generation technologies using agricultural and forestry by-products (Fischer et al. 2009).
Land degradation and the subsequent loss of productive capacity could potentially lead to an expansion of agricultural land into remaining natural habitats. Land degradation is increasingly driven by improper agricultural land use, poor soil and water management practices, deforestation, loss of natural vegetation, or excessive use of agro-chemicals, as well as, natural disasters including droughts, floods, and landslides (United Nations Environment Program [UNEP] 2002; Bruinsma 2003). According to various global land degradation assessments (Oldeman et al. 1990; UNEP 1992; Bridges & Oldeman 2010; FAO 2012), approximately 23% of all usable land (excluding mountains and deserts) has been affected by degradation to a degree sufficient to reduce its productivity. In the early 1990s, about 910 million ha of land were classified as “moderately degraded” with greatly reduced agricultural productivity and 305 million ha were classified as “strongly to extremely degraded” (UNEP 2002).
The expansion of agricultural land contributes to the loss of natural ecosystems and corresponding biodiversity losses (Koh & Ghazoul 2008). Nellemann et al. (2009) estimated that 80% of all endangered birds and mammals are threatened by agricultural expansion and unsustainable land use. In a majority of developing economies, the decline in forest and woodland area is mainly the result of land conversion to crop production (FAO 2007).
The Global Forest Resources Assessment 2000 estimated deforestation during the 1990s at 16.1 million ha per year, resulting in a loss of 4.2% of the natural forest that existed in 1990 (FAO 2001). In the period from 1981 to 1990, the area of tropical forests cleared each year in Latin America was 7.4 million ha on average. This is almost as much as the sum of deforested areas in Asia and Africa combined. During 1991 to 2000, deforestation in Latin America declined to 4.3 million ha annually (Barbier 2004). At the same time, there was an increase in the forest area as a result of aforestation, such that the net global decrease in forest area was about 9.4 million ha per year from 1990 to 2000. Overall, the total net forest change was positive for the temperate regions but negative for the tropical ones (FAO 2001).
Deforestation has various adverse effects. In 2004, carbon dioxide-equivalent emissions from deforestation, decay of biomass, and burning of peat land were estimated to be 17.3% of total emissions (International Panel for Climate Change [IPCC] 2007). In addition, tropical forests are rich in floral and faunal diversity, which is threatened by deforestation. Even though a slowdown in deforestation and rangeland clearance for crop production has been observed on a global scale, pressures on forests are likely to continue in some developing countries. Deforestation is driven by a number of site-specific causes (Geist & Lambin 2002), such as a lack of nonagricultural employment opportunities in a large proportion of rural communities (Bruinsma 2003) or unfavorable management options (e.g.. low irrigation and fertilizer rates leading to soil degradation and, consequently, expansion of agricultural lands) (Barbier 2004).
A major driving factor for deforestation is the expansion of grazing land for livestock, particularly in Latin America. About 70% of deforested land in the Amazon is now managed as pastures. On a global scale, the livestock sector is estimated to account for 78% of agricultural land and as much as 33% of the cropland. Dietary shifts toward more meat will require a much larger share of crop and grazing land for feed production, which will exert pressures on crop production for human uses (Steinfeld et al. 2006).
The literature is ambiguous on whether further agricultural land expansion is feasible or not. For instance, researchers from FAO and the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) developed an agro-ecological zones model that computes amounts of nonarable and arable land as a function of environmental constraints (Fischer et al. 2002a, b; Fischer et al. 2005). Fischer et al. (2002b) estimated that approximately 2.5 billion ha or 18.6% of land with a potential for rain-fed crop cultivation exist, of which 1.6 billion ha are located in developing countries. This estimate does not account for nonagricultural land uses such as infrastructure, settlements, or legally protected areas. However, even when excluding areas that are forests or legally protected areas, 17.6% of total terrestrial surface has a potential for arable uses (Fischer et al. 2002b). On a regional scale, it is suggested that only 22% of potentially suitable arable land in sub-Saharan Africa, 19% in Latin America, and 52% in East Asia (excluding China) was farmed from 1997 to 1999. In these regions, expansion of arable land continues to contribute to agricultural growth. In contrast, about 87% of suitable area has already been cultivated in the near East and North Africa and about 94% in South Asia (except India) (Bruinsma 2003).
Other studies conclude that much of the land suitable for agricultural production has already been developed (Khan & Hanjira 2008). For instance, Alexandratos (1995) estimated that more than 70% of the potentially available rain-fed cropland in sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America suffers from topographical, soil, and terrain constraints and therefore is not available for agricultural production. Other models predict that under severe climate change, the global amount of land suitable for agriculture will remain the same in 2080 as it was in the early 2000s (Fischer et al. 2002a, b; Parry et al. 2004). Also, Fischer et al. (2002b) concluded that there were severe limitations to their estimates of land with potential for arable uses. An increased use of cultivated land might not be feasible because of competition for land with alternative agricultural uses or severe impacts on biodiversity and the global carbon cycle. Additionally, there might be ecological constraints, low soil fertility, high incidence of crop diseases, or a lack of infrastructure and access to appropriate technologies (including economic incentives to adopt them). Socioeconomic restrictions (e.g., suitability for a particular crop that is not demanded on the domestic or foreign markets) are further limitations to the estimates of potentially available arable lands (Fischer et al. 2002b; Bruinsma 2003).
Overall, some additional land could be used for crop production, but the competition with other land uses, the desire to protect natural habitats, and the required services provided by natural ecosystems (e.g., carbon storage in rainforests and flood control) can make this an unwanted or inefficient solution (Balmford et al. 2005).
Intensification can be defined as an increase in production per unit of inputs (e.g., labor, land, time, fertilizer, seed, feed, or cash) (FAO 2004). It has permitted the doubling of the world’s food production from 1961 to 1996, with only a 10% increase in the global amount of land under cultivation (Tilman 1999). Driving forces for intensification are releasing capital and knowledge constraints, changes in the price ratios of inputs and outputs, as well as farm technologies as a function of land and water scarcity, growth in population, and investments in crop and livestock breeding that can change the quantity and value of production per ha (Lambin et al. 2001).
Even though yield growth is expected to remain the driving force of crop production, annual yield growth rates for many crops are projected to decline until 2030. The average increase in cereal yield in developing countries has declined from 2.5% per acre in the period from1961 to 1999 to 1.4% between 1991 and 2001 and is projected to decline to 1% in 2030 (Bruinsma 2003). However, there is a wide geographic variation in crop productivity, even across regions with similar natural conditions, for example because of inadequate nutrient and water management (World Bank 2008; Vitousek et al. 2009). There are institutional constraints such as limited access to knowledge and technologies to increase production, lacking finances to undertake investments (e.g., irrigation, fertilizer, soil-conservation measures), and unfavorable prospects for returns on agricultural investment. Closing the yield gap (i.e. the difference between realized productivity and the maximum attainable yield at a site given current genetic material, available technologies, and management) can substantially increase food production levels (Godfray et al. 2010; Foley et al. 2011).
The gains in agricultural productivity are often accompanied by adverse effects on natural resources and the environment, which may risk the future productive potential. Examples are land degradation through soil erosion and salinization; susceptibility to diseases; loss of genetic resources; emissions of greenhouse gases; nitrogen and phosphorus losses causing eutrophication in water aquifers; or losses of habitat and species diversity (Bruinsma 2003).
Increasing land-use intensity such as through higher fertilizer inputs and mowing frequencies as well as homogenization of landscapes reduces biodiversity (Benton et al. 2003). Globally, more than 4,000 plant and animal species are threatened by agricultural intensification (Nellemann et al. 2009). There is an ongoing debate whether the land for nature protection should be separated from the agricultural land use. It may be beneficial under certain circumstances to intensify production in some areas to reduce pressure on the native lands for nature conservation (Balmford et al. 2005; Green et al. 2005). However, one has to acknowledge that leakage and rebound effects may undermine expected land-use effects (Lambin & Meyfroidt 2011). On the other hand, for some parts of the world, such as the European Alps, extensively managed agricultural land-use systems have created semi-natural habitats of high ecological value, within which both intensification as well as land abandonment may lead to biodiversity losses (Tasser & Tappeiner 2002).
One-third of the increase in world cereal production in the 1970s and 1980s has been attributed to increased use of fertilizers (Bruinsma 2003). The other estimates based on the FAO database (FAO 2010a) suggest that between 1961 and 2007, the use of nitrogen fertilizer on a global scale increased 7.5-fold and that of phosphorus 3.3-fold (see Table 1.1).
About 40% of the global human population is dependent on synthetic nitrogen fertilizer (Smil 2002a; Stewart et al. 2005). However, its use varies among regions (Vitousek et al. 2009). In 1997 to 1999, the highest rates of fertilizer use were in East Asia (194 kg/ha of arable land), followed by the industrial countries with 117 kg/ha, whereas farmers in sub-Saharan Africa applied only 5 kg/ha on average (Bruinsma 2003). This resulted in average cereal yields in sub-Saharan Africa of 1.1 t/ha in 2000, whereas average yields in Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East/North Africa amounted to 3.7, 2.8, and 2.7 t/ha, respectively (Kelly 2006).
Table 1.1 Nitrogen and phosphate fertilizer in kg/ha arable land and permanent crops for the years 1961, 1981, 1997, 2002, and 2007.
Source: FAO (2010a).
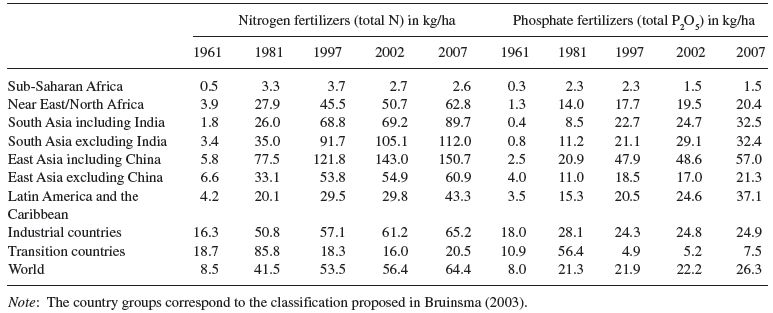
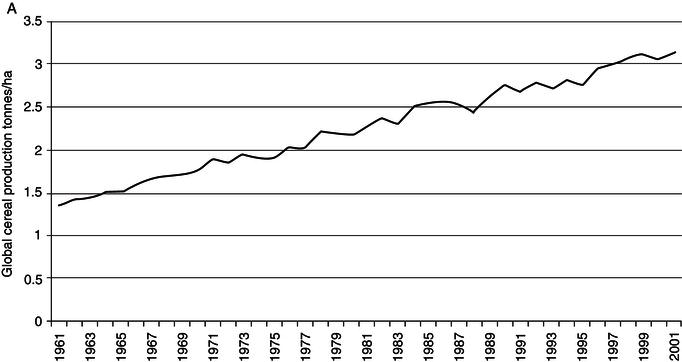
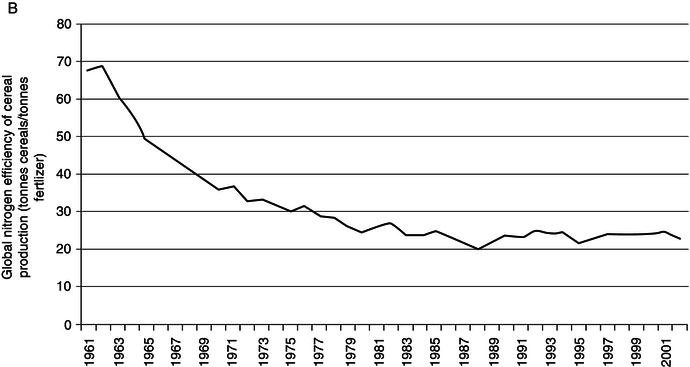
In the past decades, an increase in the consumption of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers has been observed globally (see Table 1.1). By 2050, nitrogen fertilization is expected to increase by 2.7 times and phosphorus by 2.4 times on a global scale (Tilman et al. 2001). However, increased fertilizer application rates exhibit diminishing marginal returns such that further increases in fertilizer are unlikely to be as effective in increasing cereal yield as in the past. A declining trend in global nitrogen efficiency of crop production (annual global cereal production divided by annual global nitrogen application) is shown in Figure 1.1 (Tilman et al. 2002; FAO 2010a).
It is estimated that today only 30% to 50% of applied nitrogen fertilizers (Smil 2002a; Ladha et al. 2005) and 45% of phosphorus fertilizers (Smil 2000) are used for crops. For example, only 20% to 60% of nitrogen fertilizers applied in intensive wheat production is taken up by the crop, 20% to 60% remains in the soil, and approximately 20% is lost to the environment (Pilbeam 1996). The phosphorus-use efficiency can be as high as 90% for well managed agro-ecosystems (Syers et al. 2008) or as low as 10% to 20% in highly phosphorus-fixing soils (Bolland & Gilkes 1998).
Energy is the most important resource for the production of synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. This is not the case for phosphorus fertilizers, which are produced from nonrenewable phosphate minerals. According to Cordell et al. (2009), peak phosphorus could occur by 2033. Because 90% of the rock phosphate is used for food production (Smil 2002a), a responsible handling is crucial to meet the future demand.
Even if the resource scarcity can be managed properly, there are potential adverse impacts on the environment. In regions with excessive use of fertilizers, the main environmental concerns are the off-site effects of losses to the atmosphere, as well as, surface and ground waters. The major environmental impact of phosphorus fertilization is eutrophication of surface waters. For nitrogen fertilization, these environmental impacts include eutrophication of coastal seas and lakes, loss of biodiversity and changes in species composition in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, groundwater pollution with nitrate and nitrite, and increasing greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, direct toxicity of inorganic nitrogenous compounds can severely threaten aquatic ecosystems (Smith et al. 1999; Bennet et al. 2001; Tilman et al. 2002; Rabalais 2002; Camargo & Alonso 2006).
Figure 1.1 Diminishing returns of nitrogen fertilizer application. A, Global cereal production (tonnes/ha). B, Global nitrogen fertilizer efficiency of cereal production (annual global cereal production in tonnes divided by annual global nitrogen fertilizer production in tonnes for domestic use in agriculture.)
Sources: FAO 2012a and Tilman et al. 2002.
Almost 97% of the global water resource is saltwater, 2% is snow and ice, and only 1% is available as liquid freshwater. Freshwater is mainly available as groundwater aquifers, whereas less than 2% is in rivers and lakes. Only a fraction of that is accessible for human use: an estimated 9,000 to 14,000 km3 of water is economically available each year. This represents at most 0.001% of the estimated global water resources. Agriculture is the principal user of all water resources, accounting for 70% of all withdrawals (e.g., rainfall, water from rivers, lakes, and aquifers). In comparison, 10% is assigned to domestic uses and 20% to industrial uses (FAO 2003).
On a global scale, irrigation water represents only a fifth of the total water use in agriculture (Siebert & Döll 2009), although irrigation represents up to 95% of all water withdrawals in several developing countries, which plays a major role in food production and security (Siebert et al. 2006). In sub-Saharan Africa more than 95% of the farmed land is rain-fed, in Latin America 90%, in South Asia 60%, and in the near East and North Africa 75% (FAOSTAT 2005 cited in Wani et al. 2009). However, rain-fed agriculture remains risky because of spatial and temporal variability in rainfall, water scarcity, droughts, soil erosion by wind and water, low investment, or high population pressure (Wani et al. 2009). There is a significant difference in crop yields between irrigated and rain-fed agriculture. In developing countries, grain yields from rain-fed agriculture are 1.5 t/ha compared to 3.1 t/ha from irrigated agriculture on average (Rosegrant et al. 2002).
Although there is interest in increasing the productivity of rain-fed agriculture (Turral et al. 2010), a rise in irrigated agriculture is expected in the future. In developing countries, intensively managed irrigated agriculture already accounts for 40% of total crop production from just 20% of the arable land. The share of total crop production from irrigated agriculture is expected to increase to 47% by 2030 (Bruinsma 2003).
On the downside, intensive irrigation is considered a threat to the environment, causing salinization of soils that reduces soil fertility and, hence, food production. Salinization currently affects about 10% of the world’s irrigated land (Schoups et al. 2002).
Finally, the question remains whether there will be sufficient freshwater resources to satisfy the agricultural and nonagricultural water demands (including protection of natural ecosystems) in the light of water pollution and largely unknown impacts of future climate change (Bruinsma 2003; FAO 2003). About 25% of the world’s irrigated agricultural systems have been withdrawing water above the regeneration rate, thus creating a potential for serious shortages on a local to regional scale. This trend is aggravated by poor property rights specifications on water resources and inefficient irrigation practices resulting in land degradation and reduced productivity (FAO 2008). According to the World Water Assessment Programme (2009), a few countries have the data on the purposes, quantities, and qualities of water extraction as well as the remaining resources.
Even though water scarcity is difficult to measure, analyses indicate that more than half of the world’s population lives in countries with varying degrees of water scarcity (FAO 2003). Water may be physically limited in the sense that there is no more water available, or economically, if a country cannot afford to develop additional water resources and infrastructures. It may also be caused by a lack of social adaptive capacity that prevents increasing productivity per unit water consumed (Allan 1995).
The water shortage on a global scale may be arguable. Some sources consider there is no serious threat of water shortages in the future (Bruinsma 2003), whereas others estimate that, taking environmental water requirements into account, serious water shortages are likely to occur (Smakhtin et al. 2004a, b).
Plant breeding has created modern crop and animal varieties and contributed to productivity gains in agriculture. In the future, it may contribute to producing crops that are better adapted to pests, droughts, and other environmental stresses and have a higher nutritional value. In particular, genetically modified (GM) crop species such as maize, soybean, and cotton have been commercialized in the last decade, albeit in selected countries only. In 2007, GM crops were grown on estimated 114 million ha, with more than 90% in only four countries (Argentina, Brazil, Canada, and the United States) (World Bank 2010). The GM crop area expanded to 125 million ha in 25 countries, including 15 developing countries in 2008 (James 2008) and to 160 million ha in 29 countries in 2011 (James 2011).
The GM crops are expected to lessen environmental pollution, increase crop productivity, decrease production costs, and reduce nitrous oxide emissions (World Bank 2010). However, the cultivation of GM crops remains controversial. There are ethical concerns about increasing dependency of farmers on international biotechnology companies. Furthermore, concerns about food safety and environmental risks (including possible cross-pollination with wild relatives, creation of herbicide-tolerant weeds, and evolution of new pest types that are adapted to GM plants) are among the concerns. There are also fears that diversity of agricultural crop species may further decrease as traditional cultivars are displaced by a narrow range of new GM ones (World Bank 2010).
Climate change poses serious challenges to agricultural production and calls for alternative strategies to meet increasing food demands. At the same time, the agricultural sector contributes considerably to climate change. In 2004, the agricultural sector caused about 13.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions in terms of carbon dioxide-equivalent emission, including (1) nitrous oxide (N2O) from fertilizers, (2) methane (CH4) from livestock, rice production, and manure storage as well as (3) carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning biomass. Emissions associated with the forestry sector, including land-use change, deforestation, and burning account for about 17.4% of total CO2-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions (IPCC 2007; World Bank 2010).
Climate change is expected to put conflicting pressures on agricultural production (World Bank 2010). Although it is difficult to quantify the effect of climate change on food production compared to other drivers, the occurrence of following impacts is considered to be likely.
Climate change impacts are predicted to vary across regions. For countries in the higher latitudes (such as Kazakhstan, the Russian Federation, or Ukraine), the food production potential could increase (Godfray et al. 2010). For instance, an increase in local annual temperatures of 1° to 3 °C along with enhanced CO2 fertilization (World Bank 2010) and the rainfall changes may have beneficial effects on crop yields (Fischer et al. 2002a). To take advantage of these developments, the respective countries will have to invest in institutions and infrastructure (Fay et al. 2010). However, extreme weather events can offset, or even reverse, such beneficial impacts. For instance, when the increased likelihood of extreme weather events is taken into consideration for Russia, the years with food production shortfalls are projected to triple by the 2070s (Alcamo et al. 2007). In contrast, in the low-latitude regions, even moderate temperature increases of 1° to 2 °C can reduce yields of major cereals such as rice, wheat, maize, and sorghum (Easterling et al. 2007). These shortfalls can be fully or partially compensated for by implementing adaptation measures. However, if temperatures continue to increase, productivity could decrease significantly and the effectiveness of adaptation measures could even be eliminated (Padgham 2009).
Several adaptation strategies are suggested to buffer adverse climate change effects. They include rural livelihood diversification leading to increased economic security and less reliance on climate-sensitive agricultural activities (Padgham 2009) (e.g., income diversification, or diversification toward livestock, horticulture, and specialized agricultural production). It also involves increasing the genetic variability among individual crop varieties (World Bank 2010) and improving access to new varieties and other production technologies, which can help farmers to increase productivity and better manage risks from droughts and floods (Padgham 2009).
In addition to adaptation measures, mitigation strategies are required as well, such as improved crop, grazing, and livestock management. This can include agronomic practices such as efficient nutrient use, reduced tillage, and recycling management (IPCC 2007). Agricultural practices relying on the traditional knowledge of farmers might embody a wealth of location-specific adaptation and risk management options and aim to protect soils, biodiversity, and water aquifers (International Assessment of Agricultural Knowledge, Science and Technology for Development [IAASTD] 2009; World Bank 2010). Finally, policies and institutions need to be strengthened to encourage timely implementations of adaptation and mitigation practices (Padgham 2009).
In this section, we present demand-side options to meet the increasing food demand, such as shifts in the dietary composition or reducing food wastage.
The world population is projected to rise to 9 billion people by 2050. The population in developing countries is projected to rise from 5.6 billion in 2009 to 7.9 billion in 2050, whereas population in developed countries is expected to increase from 1.23 billion to 1.28 billion (UN 2009). The increase in incomes of a large fraction of the world’s population may be accompanied by substantial increases in consumption of food as well as quantities of waste or discarded food (Henningsson 2004).
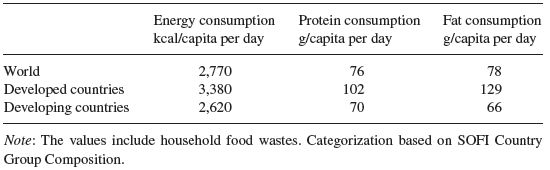
Meeting the world’s food requirements in the future may require changes in dietary patterns and composition as well as a reduction in food waste. Food intake in terms of calories, proteins, and fat differs considerably between developed and developing countries (Table 1.2), reflecting the mismatch between overconsumption of food in some regions of the world and undernourishment in others.
Table 1.2 Dietary patterns per capita in developed and developing countries as well as worldwide (2003–2005).
Source: Food and Agriculture Organization (2010b).